Is Surgery for You?
If osteoarthritis interferes significantly with everyday life and
the symptoms don't improve with physical therapy or medication, joint
replacement surgery is an option. This procedure is used on those with
severe OA and replaces a damaged joint with an artificial one. The knee
and hip are the joints that are replaced most often.Thursday, May 31, 2012
Osteoarthritis and Exercise
Osteoarthritis and Exercise
People with osteoarthritis may avoid exercise out of concern that
it will cause pain. But low-impact activities such as swimming, walking,
or bicycling can improve mobility and increase strength. Training with
light weights can help by strengthening the muscles that surround your
joints. For example, strengthening the quadriceps can reduce pain in the
knees. Ask your doctor or physical therapist which exercises are best
for you.
Labels:
osteoarthritis
Wednesday, May 30, 2012
Osteoarthritis and Weight
Osteoarthritis and Weight
If you're overweight, one of the most effective ways to relieve
pain in the knee or hip joints is to shed a few pounds. Even modest
weight loss has been shown to reduce symptoms of osteoarthritis by
easing the strain on weight-bearing joints. Losing weight not only cuts
down on pain, but may also reduce long-term joint damage.
Labels:
osteoarthritis
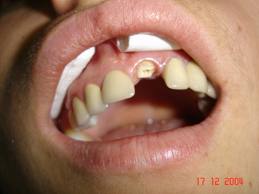
Stomatology
 Stomatology is one of the basic medical fields. It studies diagnostics, treatment and
prevention of diseases affecting teeth, oral cavity and tissues and organs
which are topographically associated with it. Stomatology services are provided
mainly in the form of an outpatient care, just a small part of the care is
provided by inpatient stomatological facilities.
Stomatology is one of the basic medical fields. It studies diagnostics, treatment and
prevention of diseases affecting teeth, oral cavity and tissues and organs
which are topographically associated with it. Stomatology services are provided
mainly in the form of an outpatient care, just a small part of the care is
provided by inpatient stomatological facilities.
Today’s
stomatology is a field that employs exclusively university-educated
professionals, i.e. doctors after graduation from five to six years long
studies at a university.
A doctor-stomatologist’s
coworkers are health services staff: a nurse, a dental technician, an X-ray
technician, and a dental hygienist.
Labels:
Stomatology
Tuesday, May 29, 2012
Medication for osteoarthritis
Medication for OA
When osteoarthritis flares up, many patients find relief with
over-the-counter pain and anti-inflammatory medication, such as aspirin,
ibuprofen, or acetaminophen. Pain-relieving creams or sprays can also
help when applied directly to the sore area. If pain persists despite
the use of pills or creams, your doctor may suggest an injection of
steroids or hyaluronans directly into the joint.
Supplements
Overall studies suggest no benefits of glucosamine and chondroitin –
supplements available at pharmacies and health food stores touted for
relieving pain and stiffness for people with osteoarthritis. Check with
your doctor before using chondroitin, especially if you take
blood-thinners.
Labels:
osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis Treatment
Physical Therapy
There is no treatment to stop the erosion of cartilage in the
joints, but there are ways to improve joint function. One of these is
physical therapy to increase flexibility and strengthen the muscles
around the affected joints. The therapist may also apply hot or cold
therapies such as compresses to relieve pain.
Supportive Devices
Supportive devices, such as finger splints or knee braces, can
reduce stress on the joints and ease pain. If walking is difficult,
canes, crutches, or walkers may be helpful. People with osteoarthritis
of the spine may benefit from switching to a firmer mattress and wearing
a back brace or neck collar.
Labels:
osteoarthritis
Diagnosing Osteoarthritis
To help your doctor make an accurate diagnosis, you'll need to describe
your symptoms in detail, including the location and frequency of any
pain. Your doctor will examine the affected joints and may order X-rays
or other imaging studies to see how much damage there is, and to rule
out other joint conditions. In many cases, blood tests are used to rule
out other forms of arthritis.
Long-Term Complications
Unlike rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis does not affect the
body's organs or cause illness. But it can lead to deformities that take
a toll on mobility. Severe loss of cartilage in the knee joints can
cause the knees to curve out, creating a bow-legged appearance (shown on
the left). Bony spurs along the spine (shown on the right) can irritate
nerves, leading to pain, numbness, or tingling in some parts of the
body.
Labels:
osteoarthritis
Monday, May 28, 2012
Osteoarthritis: Where Does It Hurt?
Where Does It Hurt?
In most cases, osteoarthritis develops in the weight-bearing joints of the knees, hips, or spine. It's also common in the fingers, thumb, neck, and big toe. Other joints are usually not affected, unless an injury is involved.What Causes It?
Every joint comes with a natural shock absorber in the form of cartilage. This firm, rubbery material cushions the ends of the bones and reduces friction in healthy joints. As we age, joints become stiffer and cartilage is more vulnerable to wear and tear. At the same time, repetitive use of the joints over the years irritates the cartilage. If it deteriorates enough, bone rubs against bone, causing pain and reducing range of motion.Risk Factors You Can't Control
One of the major risk factors for osteoarthritis is something none of us can control – getting older. Gender also plays a role. Over age 50, more women than men develop osteoarthritis. In most cases, the condition results from normal wear and tear over the years. But some people have a genetic defect or joint abnormality that makes them more vulnerable.
Labels:
osteoarthritis
Saturday, May 26, 2012
Osteoarthritis Symptoms
Osteoarthritis Symptoms
The symptoms of osteoarthritis tend to develop slowly. You may notice pain or soreness when you move certain joints or when you've been inactive for a prolonged period. The affected joints may also be stiff or creaky. Typically, osteoarthritis leads to morning stiffness that resolves in 30 minutes. When osteoarthritis affects the hands, some people develop bony enlargements in the fingers, which may or may not cause pain. |
| osteoarthritis-overview-s2-knee-pain |
Labels:
osteoarthritis
Pictures of Osteoarthritisost
Osteoarthritis: What Is It?
Also called "wear and tear" arthritis or degenerative joint disease, osteoarthritis (OA) is the progressive breakdown of the joints' natural shock absorbers. This can cause discomfort when you use the affected joints –- perhaps an ache when you bend at the hips or knees, or sore fingers when you type. Most people over 60 have some degree of OA, but it also affects people in their 20s and 30s.
osteoarthritis-overview-s1-xray-knee
osteoarthritis-overview-s3-joint-xrays
osteoarthritis-overview-s4-illustration-femur-osteoarthritis
osteoarthritis-overview-s8-doctor-patient-xray-computer
osteoarthritis-overview-s9-bow-legged-bone-spurs-spine
osteoarthritis-overview-s10-physical-therapy
osteoarthritis-overview-s11-knee-brace
Also called "wear and tear" arthritis or degenerative joint disease, osteoarthritis (OA) is the progressive breakdown of the joints' natural shock absorbers. This can cause discomfort when you use the affected joints –- perhaps an ache when you bend at the hips or knees, or sore fingers when you type. Most people over 60 have some degree of OA, but it also affects people in their 20s and 30s.
osteoarthritis-overview-s1-xray-knee
osteoarthritis-overview-s3-joint-xrays
osteoarthritis-overview-s4-illustration-femur-osteoarthritis
osteoarthritis-overview-s8-doctor-patient-xray-computer
osteoarthritis-overview-s9-bow-legged-bone-spurs-spine
osteoarthritis-overview-s10-physical-therapy
osteoarthritis-overview-s11-knee-brace
Labels:
osteoarthritis
Tuesday, May 22, 2012
What is the prognosis for knee pain ?
The outlook for an individual with knee pain depends on the particular
cause of the pain. For examples, knee pain caused by degenerative
cartilage can be chronic, while knee pain from injury sometimes resolves
completely with appropriate treatment.
he following tips generally help prevent or reduce pain. Check with you physician for specific recommendations for your situation:
Can knee pain be prevented?
Knee pain can be prevented only to the extent that injuries can sometimes be avoided can knee pain be prevented.he following tips generally help prevent or reduce pain. Check with you physician for specific recommendations for your situation:
- Increase Training Gradually : Doing too much too soon, is one of the major causes of sports injury Knee pain is particularly common in runners who increase training mileage quickly. The best way to avoid this is to follow the 10 percent rule. This simply means that you should limit your training increases to a maximum of 10 percent each week. That cane be time, load, mileage or any other parameter.
- Strengthening Exercises : Muscle weakness or imbalance is one of the first things physical therapists check for when evaluating knee pain. Such an imbalance can be the source of pain. In addition to specific muscle strengthening of the muscles that support the knee (quads, hamstrings, calf), building core strength improves overall stability which may reduce the risk of injury
- Skills Training : oordination drills and proprioceptive training have also been found to be helpful in protecting the knee from injuries
- Appropriate Footwear : using the correct footwear is helpful to control excess ankle motion
Sunday, May 20, 2012
What are diseases and conditions that can cause knee pain, and what is the treatment for this knee pain?
Pain can occur in the knee from
diseases or conditions that involve the knee joint, the soft tissues and bones
surrounding the knee, or the nerves that supply sensation to the knee area. In
fact, the knee joint is the most commonly involved joint in rheumatic diseases,
immune diseases that affect various tissues of the body including the joints to cause arthritis.
Arthritis is inflammation within a joint. The causes of knee joint inflammation range from noninflammatory types of arthritis such as osteoarthritis, which is a degeneration of the cartilage of the knee, to inflammatory types of arthritis (such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout). Treatment of the arthritis is directed according to the nature of the specific type of arthritis. Many people suffer from arthritis; the pain and discomfort can be so limiting that some patients may require a total knee joint replacement. Knee replacement surgery often allows the patient to regain much of their mobility.
Swelling of the knee joint from arthritis can lead to a localized collection of fluid accumulating in a cyst behind the knee. This is referred to as a Baker cyst and is a common cause of pain at the back of the knee.
Infections of the bone or joint can rarely be a serious cause of knee pain and have associated signs of infection including fever, extreme heat, warmth of the joint, chills of the body, and may be associated with puncture wounds in the area around the knee. These infections are often diagnosed by aspirating joint fluid accumulations with a needle (joint aspiration) and examining the fluid microscopically and with microbial culture techniques. Treatment involves antibiotics and sometimes joint surgery.
Arthritis is inflammation within a joint. The causes of knee joint inflammation range from noninflammatory types of arthritis such as osteoarthritis, which is a degeneration of the cartilage of the knee, to inflammatory types of arthritis (such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout). Treatment of the arthritis is directed according to the nature of the specific type of arthritis. Many people suffer from arthritis; the pain and discomfort can be so limiting that some patients may require a total knee joint replacement. Knee replacement surgery often allows the patient to regain much of their mobility.
Swelling of the knee joint from arthritis can lead to a localized collection of fluid accumulating in a cyst behind the knee. This is referred to as a Baker cyst and is a common cause of pain at the back of the knee.
Infections of the bone or joint can rarely be a serious cause of knee pain and have associated signs of infection including fever, extreme heat, warmth of the joint, chills of the body, and may be associated with puncture wounds in the area around the knee. These infections are often diagnosed by aspirating joint fluid accumulations with a needle (joint aspiration) and examining the fluid microscopically and with microbial culture techniques. Treatment involves antibiotics and sometimes joint surgery.
Wednesday, May 16, 2012
What injuries can cause knee pain, and what are symptoms? How is knee pain with injury diagnosed and treated?What injuries can cause knee pain, and what are symptoms? How is knee pain with injury diagnosed and treated?
What injuries can cause knee pain, and what are symptoms? How is knee pain with injury diagnosed and treated?
Injury can affect any of the ligaments, bursae, or tendons surrounding
the knee joint. Injury can also affect the ligaments, cartilage,
menisci
(plural for meniscus), and bones forming the joint. The complexity of
the design of the knee joint and the fact that it is an active
weight-bearing joint are factors in making the knee one of the most
commonly injured joints.
Ligament injury
Trauma can cause injury to the ligaments on the inner portion of the knee (medial collateral ligament), the outer portion of the knee (lateral collateral ligament), or within the knee (cruciate ligaments). Injuries to these areas are noticed as immediate pain but are sometimes difficult to localize. Usually, a collateral ligament injury is felt on the inner or outer portions of the knee. A collateral ligament injury is often associated with local tenderness over the area of the ligament involved. A cruciate ligament injury is felt deep within the knee. It is sometimes noticed with a "popping" sensation with the initial trauma. A ligament injury to the knee is usually painful at rest and may be swollen and warm. The pain is usually worsened by bending the knee, putting weight on the knee, or walking. The severity of the injury can vary from mild (minor stretching or tearing of the ligament fibers, such as a low grade sprain) to severe (complete tear of the ligament fibers). Patients can have more than one area injured in a single traumatic event.
Monday, May 14, 2012
What are risk factors for knee pain ?
What are risk factors for knee pain ?
Risk factors for knee pain include aging, athletic activities, and trauma injuries. Occasionally, it is associated with swelling and warmth in the knee.
The meniscal tear can be diagnosed in one of three ways: arthroscopy, arthrography, or an MRI. The complexity of the design of the knee joint and the fact that it is an active weight-bearing joint are factors in making the knee one of the most commonly injured joints. It is generally recommended to avoid bearing weight on the injured joint, and crutches may be required for walking.
Labels:
Arthritis
,
knee pain
,
risk factors
,
treatment
Saturday, May 12, 2012
How is the knee designed, and what is its function?
The knee joint has an inner (medial) and an outer (lateral) compartment. . This joint has an inner (medial) and an outer (lateral) compartment. The thighbone (femur) meets the large shinbone (tibia), forming the main knee joint. The meniscus acts as a smooth surface for motion and absorbs the load of the body above the knee when standing. The meniscus is a thickened cartilage pad between the two joints formed by the femur and tibia. The large muscles of the thigh move the knee. Below the kneecap, there is a large tendon (patellar tendon) which attaches to the front of the tibia bone. . There are large blood vessels passing through the area behind the knee (referred to as the popliteal space).
The knee is a weight-bearing joint. The goal of this article is to give the reader an overview of causes of knee pain. Each meniscus serves to evenly load the surface during weight-bearing and also aids in disbursing joint fluid for joint lubrication. For example, bursitis, types of arthritis, total knee replacement, and others are covered in articles devoted to knee pain-related topics that include specifics on diagnosis, tests, treatments, and other details. The knee is a weight-bearing joint. Most of the topics covered in this article are further expanded in detail as separate articles. The bursae, or fluid-filled sacs, serve as gliding surfaces for the tendons to reduce the force of friction as these tendons move. Most of the topics covered in this article are further expanded in detail as separate articles. The goal of this article is to give the reader an overview of causes of knee pain. Each meniscus serves to evenly load the surface during weight-bearing and also aids in disbursing joint fluid for joint lubrication.
Thursday, May 10, 2012
Knee pain facts
Knee pain facts
Knee pain is a common complaint that affects people of all ages. Many types of minor knee pain respond well to self-care measures. . Physical therapy and knee braces also can help relieve knee pain. Medical conditions — including arthritis, gout and infections — also can cause knee pain. Physical therapy and knee braces also can help relieve knee pain. Knee pain may be the result of an injury, such as a ruptured ligament or torn cartilage. Knee pain may be the result of an injury, such as a ruptured ligament or torn cartilage. Knee pain may be the result of an injury, such as a ruptured ligament or torn cartilage. Many types of minor knee pain respond well to self-care measures.
Causes
InjuriesA knee injury can affect any of the ligaments, tendons or fluid-filled sacs (bursae) that surround your knee joint as well as the bones, cartilage and ligaments that form the joint itself. The meniscus is formed of tough, rubbery cartilage and acts as a shock absorber between your shinbone and thighbone. Knee bursitis. Some knee injuries cause inflammation in the bursae, the small sacs of fluid that cushion the outside of your knee joint so that tendons and ligaments glide smoothly over the joint. An ACL injury is particularly common in people who play basketball or go downhill skiing, because it's linked to sudden changes in direction. Knee bursitis. An ACL injury is the tearing of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) — one of four ligaments that connect your shinbone to your thighbone. It can be torn if you suddenly twist your knee while bearing weight on it. Tendinitis is irritation and inflammation of one or more tendons — the thick, fibrous cords that attach muscles to bones. An ACL injury is particularly common in people who play basketball or go downhill skiing, because it's linked to sudden changes in direction.
Mechanical problems
This may not create any problems unless the loose body interferes with knee joint movement — the effect is something like a pencil caught in a door hinge. ' This can occur from a cartilage tear. This occurs when the triangular bone (patella) that covers the front of your knee slips out of place, usually to the outside of your knee. You'll be able to see the dislocation, and your kneecap is likely to move excessively from side to side. Dislocated kneecap. This occurs when the triangular bone (patella) that covers the front of your knee slips out of place, usually to the outside of your knee. In some cases, problems in the hip or foot can refer pain to the knee. Hip or foot pain. ' This can occur from a cartilage tear. Mechanical problem sLoose body.
Types of arthritis
Sometimes your knee joint can become infected, leading to swelling, pain and redness. Although rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease, it tends to vary in severity and may even come and go. Although rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease, it tends to vary in severity and may even come and go. Gout. Sometimes called degenerative arthritis, osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis. Gout. Although rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease, it tends to vary in severity and may even come and go. Osteoarthritis. Sometimes your knee joint can become infected, leading to swelling, pain and redness. Septic arthritis often occurs with a fever
.
Monday, May 7, 2012
About knee Pain
Information about knee pain causes and treatment
Knee pain is an extremely common complaint, and there are many causes. It is important to make an accurate diagnosis of the cause of your symptoms so that appropriate treatment can be directed at the cause. If you have knee pain, some common causes include
- Knee pain facts
- How is the knee designed, and what is its function?
- What are risk factors for knee pain?
- What injuries can cause knee pain, and what are symptoms? How is knee pain with injury diagnosed and treated?
- What are diseases and conditions that can cause knee pain, and what is the treatment for knee pain?
- What is the outlook (prognosis) for knee pain?
- Can knee pain be prevented?
- Pictures of Osteoarthritis: A Visual Guide to OA - Slideshow
- Exercises for OA of the Knee - Slideshow
- Take the Pain Quiz!
- Patient Discussions: Knee Pain - Treatments
- Patient Discussions: Knee Pain - Length Symptoms Lasted
Labels:
Arthritis
,
knee pain
,
Orthopedics Ads
,
treatment
Friday, May 4, 2012
medical home care
Protect yourself and your ancestors with the appropriate
accessories and food for situations that may appear in the home. Acquisition a
reliable supplier, analyze the types of items that may be all-important for
circadian aboriginal aid, advancing treatment, authoritative potentially adverse
bacteria, and accumulate yourself and your ancestors advantageous and happy.
You charge to apperceive that the articles you shop for are top
quality, fabricated by manufacturers you apperceive and trust.
You charge accessible online acclimation and fast shipping,
beeline to your door.
And you charge aloof one reliable supplier who can do it all.
Mountainside Medical is the answer
the home medical bloom food we stock:
Diabetes administration
Health accessories
Bathroom assurance
Mobility aids
Incontinence affliction
Patient allowance food
Wound affliction
Home respiratory affliction
Physiotherapy aids
Blood burden accessories
To acquisition the home medical food you need, use the
accessible card to the larboard or the chase agent to the high
right
 |
| Commode Fold Steel. |
 |
| Folding Bath Bench |
 |
| Wheelchair |
Tuesday, May 1, 2012
Hospital Products Share
Hospital Products Share:
Supplier, Manufacturer and Wholesaler of Hospital Products such as Bedside Screen, Hospital Equipment and Saline Stand.
1-Bedside Screen
bedside awning which has tubular anatomy in three sections. Designed in acquiescence with all-embracing affection standard, our artefact is broadly acclimated in hospitals, hotels, aerodynamics and railways. The bed ancillary awning consists of 50 mm dia revolving casters to ensure accessible mobility. It has springs and hooks and additionally accessible in four folds.
2-Hospital Equipment
a advanced ambit of hospital accessories appropriate for assorted units there. Some of the featured articles bogus by us are:
•Mobility aids sales & casework action hospital equipment
•ICU bed
•Fowler’s bed, semi fowler’s bed, apparent hospital bed
•Stretcher trolley – stainless steel
•Step stool
3-Saline Stand
acrid angle which is pretreated and adhesive crumb coated. It has tubular anatomy with abundant casting adamant abject with chrome platted acrid rod. Available in three legs, four legs with or after 50 mm dia with revolving casters, our ambit accommodated the claim of all-embracing standard.
Labels:
hospital equipment
,
Hospital Products Share
hospital equipment
here are abounding medical accessories acclimated in the hospital to accurately diagnosed our sickness. Abounding of them are actual expensive. That's the acumen why best hospitals today allegation big-ticket bills for their account to patients.
this blog, I altercate some of the avant-garde medical accessories of today acclimated by abounding hospitals to analyze accurately the affection of patients. Some of them are accepted and others is not been heard by abounding of us.
The most common medical equipment are:
CT scanner
Anesthesia Monitors
Anesthesia Workstations
Autoclaves / Sterilizers
Beds/Stretchers
BioZ Machines / ICG Monitor
Blood Analyzers
Blood Pressure Monitors
Bone Densitometers
Capnography
Defibrillator
Dental Equipment
EKG / ECG Machines
Echocardiography
Electrosurgical Units
Fetal Monitors
Incubators / Isolettes
Infusion Pumps
MRI Machines
Mammography Machines
Miscellaneous
Patient Monitors
Portable Ultrasound Machines
Power Wheelchairs
Pulse Oximeters
Spirometers
Stress Test EKGs
Ultrasound Machines
Ultrasound Probes / Transducers
X-Ray Machine
Anesthesia Monitors
Anesthesia Workstations
Autoclaves / Sterilizers
Beds/Stretchers
BioZ Machines / ICG Monitor
Blood Analyzers
Blood Pressure Monitors
Bone Densitometers
Capnography
Defibrillator
Dental Equipment
EKG / ECG Machines
Echocardiography
Electrosurgical Units
Fetal Monitors
Incubators / Isolettes
Infusion Pumps
MRI Machines
Mammography Machines
Miscellaneous
Patient Monitors
Portable Ultrasound Machines
Power Wheelchairs
Pulse Oximeters
Spirometers
Stress Test EKGs
Ultrasound Machines
Ultrasound Probes / Transducers
X-Ray Machine
and many more...
Please visit our site frequently to learn more about the uses of this medical equipment.
 |
| Anesthesia Workstations |
 |
| Anesthesia Monitors |
Labels:
hospital equipment
Subscribe to:
Posts
(
Atom
)